Client
Well Aware, UNC Gillings School of Global Public Health
Services
Mobile, Healthcare, UX/UI, and AI/Machine Learning
More than 42 million people are reliant on private wells for their water consumption in the United States. In North Carolina alone, approximately 2.4 million residents use private wells for their water consumption, and fewer than 200,000 have tested for contaminants. Well water can be particularly susceptible to contaminants such as microbial life, lead, and arsenic. And unlike piped water, there is no mandated oversight by the federal government to regulate private wells, leaving well owners solely responsible for testing and treating their water.
Researchers at the UNC Gillings School of Global Public Health sought to build a freely available mobile app paired with a low-cost at-home testing kit to help well owners in rural and under-resourced areas of North Carolina assess their water for contaminants. CrossComm partnered with the research team to develop a mobile app that uses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to determine the risks and concentration of microbes, lead, and arsenic in well water.
Our Approach
Utilizing Machine Learning to Solve a Real-World Problem
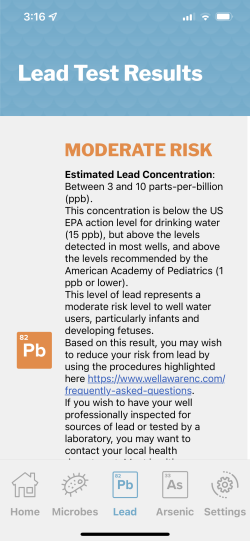
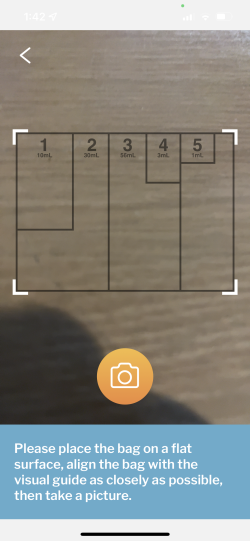
CrossComm applied multiple AI methodologies and worked with the researchers to utilize the appropriate mathematical models to derive accurate results for the mobile water testing system. The E. coli microbe test features a machine learning model that becomes smarter with each use. The arsenic and lead tests use computer vision and gradient descent to determine color value distributions in visual images of test strips. These distributions are then fed into the research team’s AI models to classify water contaminants. The results are then translated to an informative and simple interface on the mobile app where users can view the levels of risk and estimated concentration for each contaminant in their well water.
Partnering to Leverage Data into a Practical Mobile Application
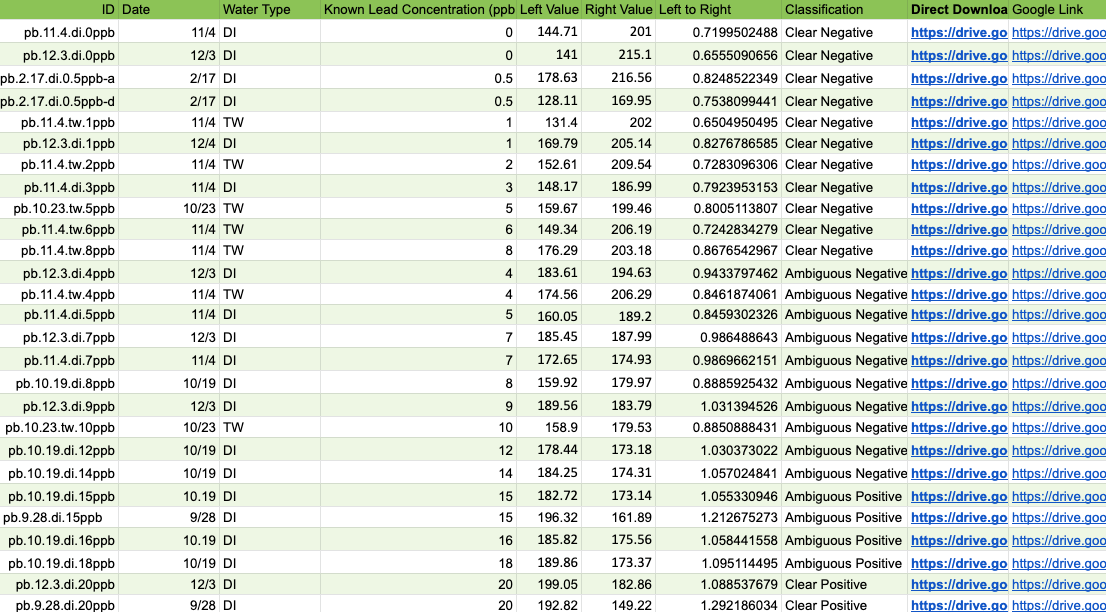
The research team provided CrossComm with pre-existing real-world datasets containing test strip images and their associated contaminant values to analyze for the concentration of lead, arsenic, and microbes. The data consisted of numerical, categorical, and test strip images which were analyzed via ImageJ, a popular scientific tool that can measure pixel value statistics, including RGB values, angles, distances, and density histograms.
CrossComm built the mobile app to apply the AI models which could ingest test strip images and determine estimated concentration and risks for all three tests. In collaboration with the researchers, the RGB colors and contaminant values from the test strip datasets were used to build a ML regression model that could detect the lead and arsenic in well water.
For the E. coli microbe test, a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) method called Mask R-CNN was used in the image recognition and processing of the test strips. With Mask R- CNN, the computer vision task of image segmentation could be accomplished, and the layers allowed for the identification and machine recognition of key variables in the test strip that indicate the presence of microbes.
Leveraging data to determine the ML models that output accurate test results, the Well Aware mobile app can now empower well water owners to make decisions to improve the quality of their water.
Results
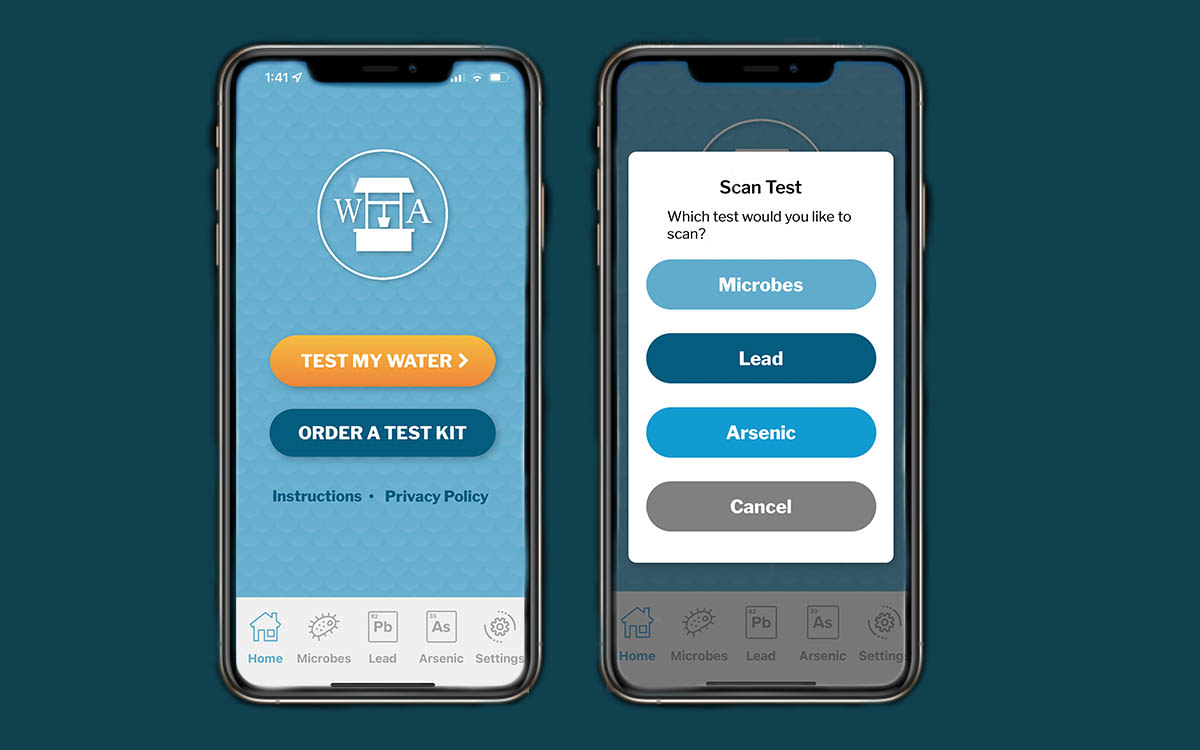
The mobile app CrossComm built effectively utilized machine learning and computer vision to produce accurate results about well water contaminants. The implications for such an application has wide-reaching social impact, especially for rural and under-resourced communities who may have limited access to water infrastructure and lab testing services. Moreover, the app has the option for users to participate in citizen science mode, allowing individuals to gather their water data and contribute to improved quality water monitoring around the world.
The test kits are available on the Well Aware website and the mobile app can be downloaded on the Apple App Store and Google Play. In the long-term, CrossComm and Well Aware researchers hope to make the app globally available so that any community can use it to test questionable or vulnerable drinking water.
If you’re interested in taking the next step in your ML project or idea, we would love to hear from you and discuss whether CrossComm would be the right technology development team for you. Tell us more and receive a free assessment from CrossComm.